

- #CREATE A VIRTUAL OPTICAL DISK FILE HOW TO#
- #CREATE A VIRTUAL OPTICAL DISK FILE INSTALL#
- #CREATE A VIRTUAL OPTICAL DISK FILE ISO#
- #CREATE A VIRTUAL OPTICAL DISK FILE DOWNLOAD#
You don’t need to burn the ISO image onto a DVD disk as you would for installing an operating system on a physical machine. Otherwise the Ubuntu installer may hang on some installation steps, keyboard may not response etc. In the Settings window, go to the Display section and select the Screen tab. Select your new VM ( Ubuntu18圆4 in this case) and click Settings ( Machine > Settings or press Ctrl+S). You need to edit VM settings after VM creation.
#CREATE A VIRTUAL OPTICAL DISK FILE INSTALL#
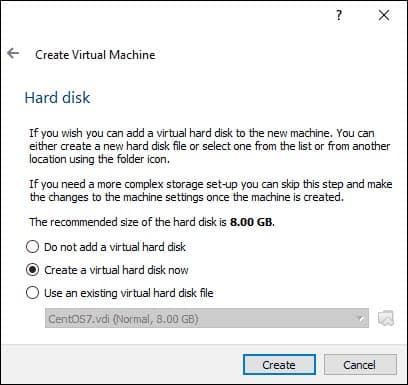
Hit Create to finish creating a new VM to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox.Ī new virtual machine to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox has now been created and its name is displayed in the list of VMs in the main VirtualBox window. This option allows you to save space on your physical disk until the virtual disk grows to its maximum allocated size. Storage on physical hard disk: Dynamically allocated. Let’s select the native VirtualBox virtual disk format. Hard disk file type: VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image). The file size of the virtual disk: 20 GB or more. On the next Create Virtual Hard Disk screen, set the virtual disk file location, for example,Ĭ:\Virtual\VirtualBox\Ubuntu18圆4\Ubuntu18圆4.vdi Select the Create a virtual hard disk now option. You should leave enough memory for your host operating system to operate normally. As our physical machine used in this example has 16 GB of RAM, we can set 4 GB of RAM for a virtual machine to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox. Machine Folder: C:\Virtual\VirtualBox (try to use disk D, E or other non-system partitions if you have them). In our example of installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox, the new VM options are the following: In the Create Virtual Machine screen, set the options for a new VM. In order to create a new virtual machine for installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox, open VirtualBox and click New ( Machine > New) or press Ctrl+N. Ubuntu 18 is provided only as 64-bit editions. In our case, the file name is ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso. Ubuntu LTS is more widely tested, enterprise-focused and compatible with new hardware.Ĭlick the green Download button and save the ISO file to the custom location. Five-year support is provided for Ubuntu LTS distributions (both Ubuntu Desktop and Ubuntu Server).

You can find version numbers that are higher than 18.04.2, but they may not offer long term support yet.
#CREATE A VIRTUAL OPTICAL DISK FILE DOWNLOAD#
Let’s download Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS – this is the latest long term support (LTS) Ubuntu version available at this moment. Go to the official Ubuntu website and download the necessary version of the Ubuntu installer. You need to download the Ubuntu distribution for installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox.
#CREATE A VIRTUAL OPTICAL DISK FILE HOW TO#
This point is especially important if you are looking for how to install Ubuntu 64-bit on VirtualBox. Your CPU (Central Processor Unit) must support Intel VT-x or AMD-v hardware virtualization features which must also be enabled in UEFI/BIOS. In order to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox, you should have a physical computer with at least 4 GB of RAM (Random Access Memory), a hard disk drive with at least 30 GB of free space (SSD is preferred due to its higher performance). Make sure that VirtualBox is installed on your physical machine before proceeding. The operating system (OS) runs on a physical machine is referred to as a host OS, and the operating system run on a VM is called a guest OS (Ubuntu in this case). Today’s blog post explains how to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox. Installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox as a virtual machine (VM) has a lot of advantages – you can create a snapshot and roll back changes to the appropriate VM state if something goes wrong, clone a VM, copy a VM to another machine easily (all VM data is stored as a set of files), or run a VM on different host operating systems that are supported by VirtualBox. Whether you are looking to try out some software, prepare for migration to Linux from Windows or macOS, test applications, network, or otherwise, you need to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox. By Michael Bose How to Install Ubuntu on VirtualBox: Detailed Overview


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
